Pleural Effusion Cat X Ray
Pleural effusions may result from pleural, parenchymal, or extrapulmonary disease. Recovered from pleural effusion frm pneumonia 12 days ago but still having pleurisy.is it normal?ctscan, xray, cbc, tibc, ana, ferittin, tb shows normal answered by dr.

Pleural Effusion Chest Xray X ray, Pleural effusion
The recognition that the disease is actual within the pulmonary parenchyma and not in the pleural space, extrathoracic structures or the mediastinum is the first step.

Pleural effusion cat x ray. A sample of pleural fluid obtained by piercing the cat's chest cavity with a needle will be sent to the laboratory for analysis. In general, the pleural (lining of the lungs) may become inflamme. The bottom red arrow points to the posterior vena cava, bringing venous blood from the back of the body to the heart.
Use the degree of mediastinal shift to determine preponderance of effusion vs. A pleural rub is also usually present, which is a grating sound heard in the chest. Pulmonary patterns have the bane of radiology since the beginning (1896 that is).
Use the meniscus sign to identify a pleural effusion. The prevalence of pleural thickening was 3.2% (n = 911/28,727) in our sample. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality.
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from disruption of the homeostatic forces responsible for the movement of pleural fluid. Get prescriptions or refills through a video chat, if the doctor feels. Video chat with a u.s.
They’ll also examine the cat, listen to its chest, and take blood and urine test. Pleural effusion is the presence of any type of fluid within the pleural space (transudate, modified transudate and exudate). Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity.
N = 1423) that was identified in 911 individuals. Pleural thickening was the most common finding (35.2%; Cat, pleural effusion, thoraccocentesis introduction pleural empyema (pyothorax) is a condition of septic exudate accumulation in the.
Infection, heart failure, cancer, inflammatory conditions such as lupus, cirrhosis, post heart surgery, pulmonary embolism (clots to the lungs) amongst other causes. The cytology came b … read more Acquiring a fluid sample might also be a key in determining the cause of the pleural effusion in cats.
Approximately 1 million people develop this abnormality each year in the united states. Healthtap doctors are based in the u.s., board certified, and available by text or video. On lateral views, ventral pleural effusion will frequently obscure the cranioventral margin of the heart.
If a pleural effusion is suspected, an individual may have to undergo a ct scan for confirmation. The most difficult concept to teach and the most difficult to learn, yet, the pattern itself is only part of the puzzle. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes, including diseases of the heart, lungs, or other systemic diseases.
Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid, shallow breathing and pet owners may. In pleural effusion, the fluid is not found within the lungs, but instead within the pleural sac. A pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid between the layers of pleura that cover the lung.
The top red arrow points to the aorta. Colds and coughs, stomach symptoms, bladder infections, rashes, and more. If the fast ultrasound does reveal pleural effusion, thoracentesis can be carried out.
The type of pleural fluid withdrawn will enable your veterinarian to diagnose the cause of the pleural effusion.
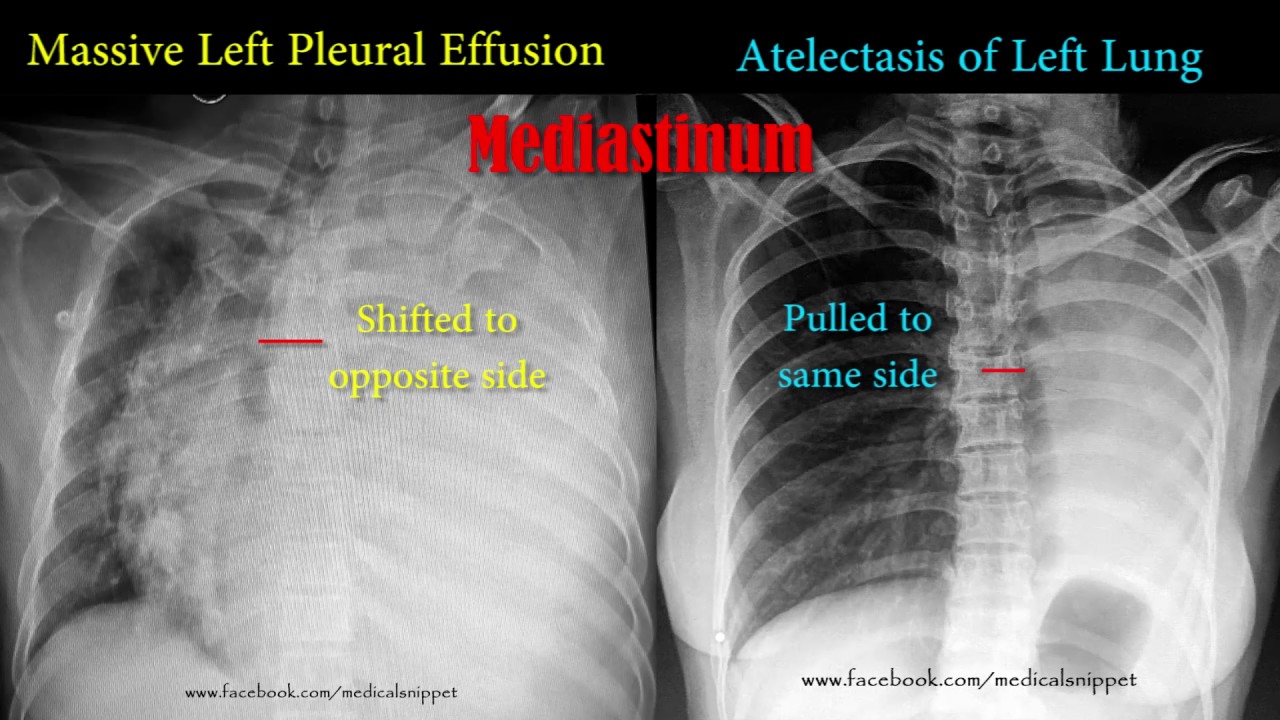
pleural effusion vs atelectasis

Pulmonary tuberculosis Radiology Case

A detailed understanding of the structures that make up

Miliary tuberculosis Radiology Case

Pneumonia Xray Pictures (With images) X ray, Pneumonia

World of XRay on Instagram “Pleural effusion is fluid in

Pin by nonas arc on Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated

139 best images about Radiologychest on Pinterest

Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma Persistent consolidation

Pin by Joan Murphy on cxr Radiology, Pet ct, Pericardial

Pin by Narcizo Ruiz Ruiz on Anatomía Anatomy bones, X

59yearold man with loculated fluid in the left major

Cavitating infection Right upper lobe

Pin by pinaki on Lund disease Lung disease, Radiology

Chest XRay Basic Interpretation X ray, Anatomy bones

Pin by Sekar Mac on xray X ray, Pericardial effusion

Acute eosinophilic pneumonia The patient shown below

Pin by Mandeep Singh on cxr Pericardial effusion

No comments: